
Uniform Circular Motion
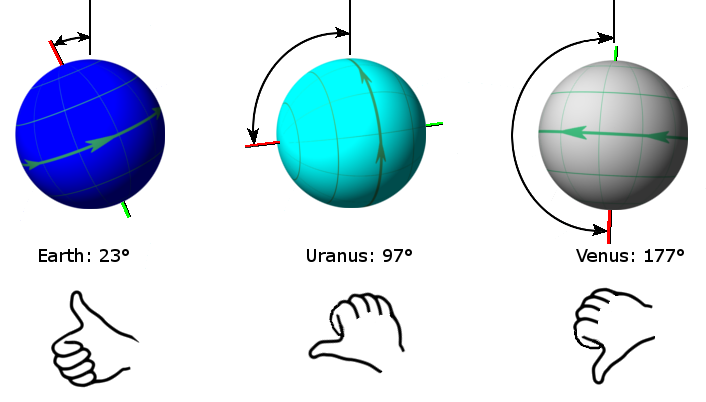
Axis of Rotation
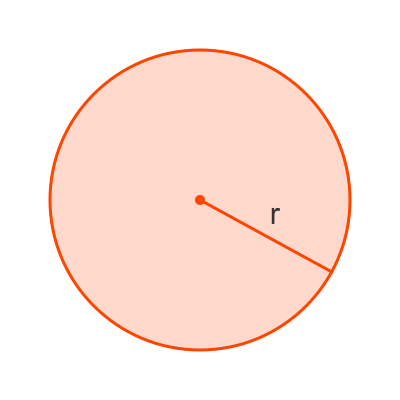
Radius

Circumference
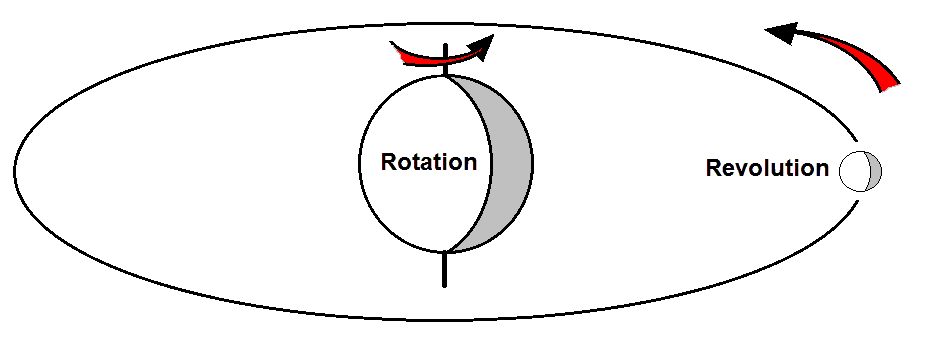
Revolution

Rotation

Rotational Speed
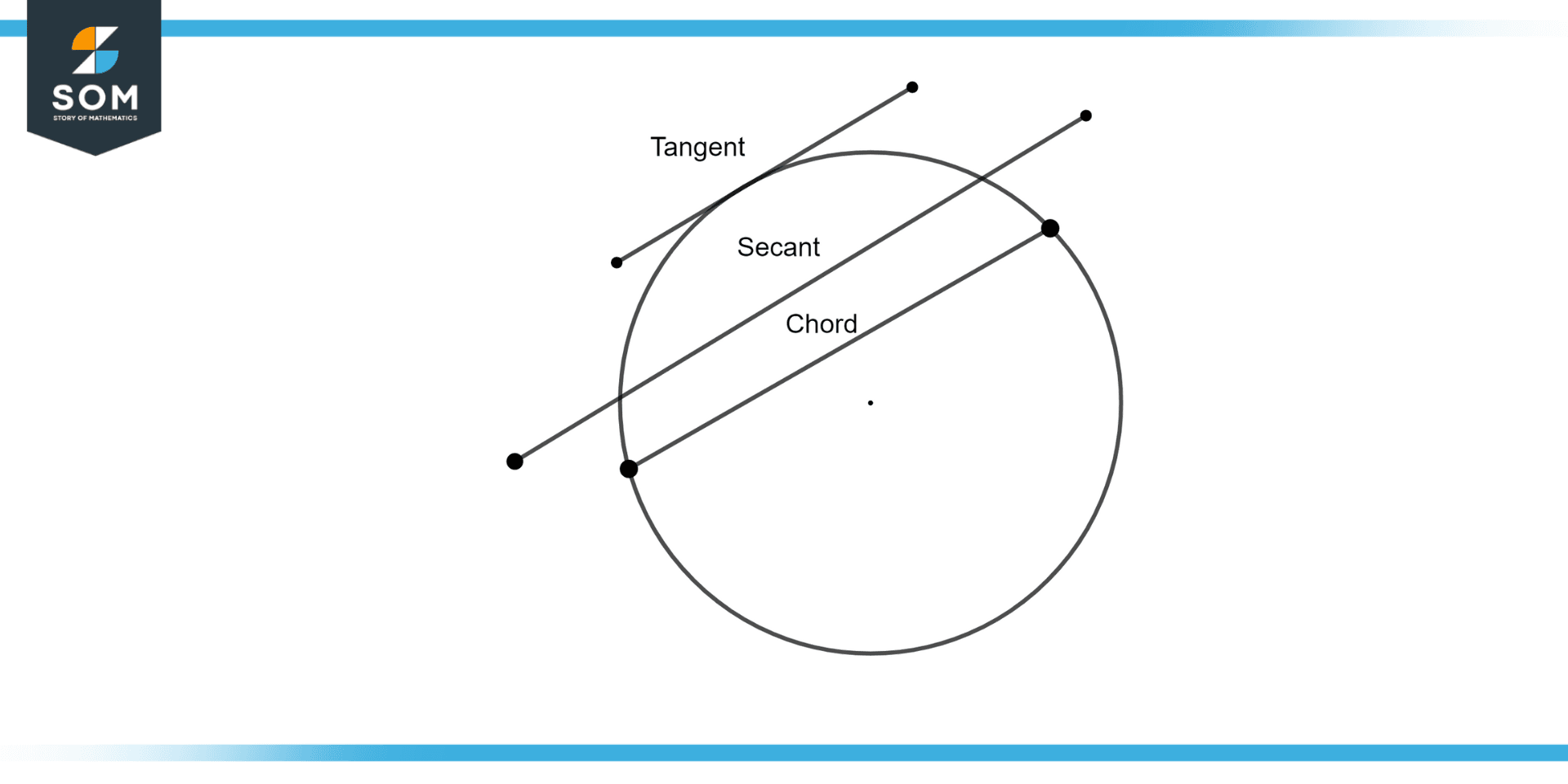
Tangent Line
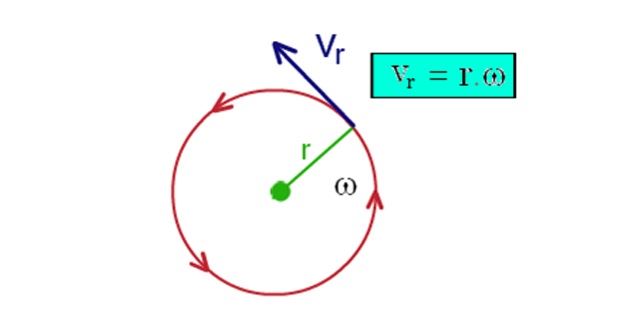
Tangential Speed / Velocity

Centripetal
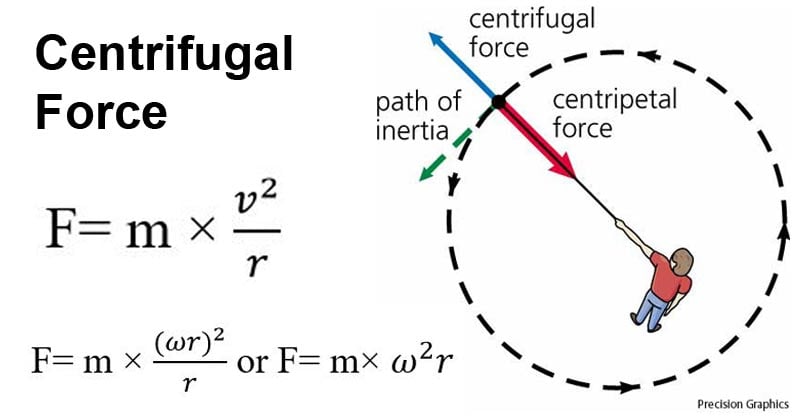
Centrifugal
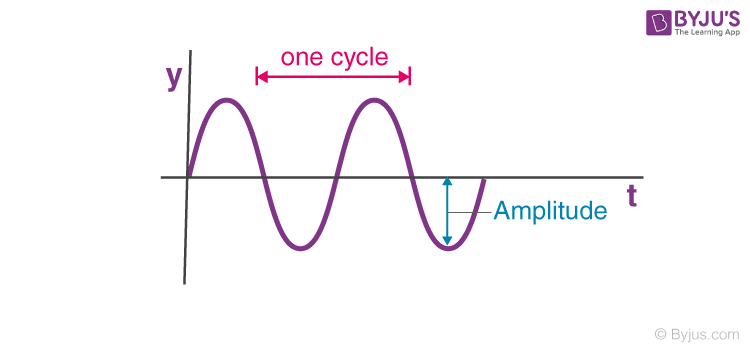
Period

Frequency
